CSIT_Labs
Recursion
Recursion means "defining a problem in terms of itself".
Recursion is a very important concept in computer science.
Programs:
Factorial
The factorial of a positive number n is given by:
factorial of n (n!) = 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 *... * n
- The factorial of a negative number doesn’t exist.
- The factorial of 0 is 1.
Fibonacci
The Fibonacci sequence is a sequence of numbers where the first two numbers are 0 and 1.
The Fibonacci numbers are the numbers in the following integer sequence. 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, ……..
In mathematical terms,
- the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence relation
fn = fn-1 + fn-2
- with seed values
f0 = 0 and f1 = 1.
G.C.D
Greatest Common Divisor (G.C.D) is the largest number that divides both the given numbers without a remainder.
A simple and old approach is Euclidean algorithm by subtraction
It is is a process of repeat subtraction, carrying the result forward each time until the result is equal to the any one number being subtracted. If the answer is greater than 1, there is a GCD (besides 1). If the answer is 1, there is no common divisor (besides 1), and so both numbers are coprimes
pseudo code for above approach:
int gcd(a, b){
if (a == b)
return a
if (a > b)
gcd(a – b, b)
else
gcd(a, b – a)
}
At some point one number becomes factor of the other so instead of repeatedly subtracting till both become equal , we check if it is factor of the other .
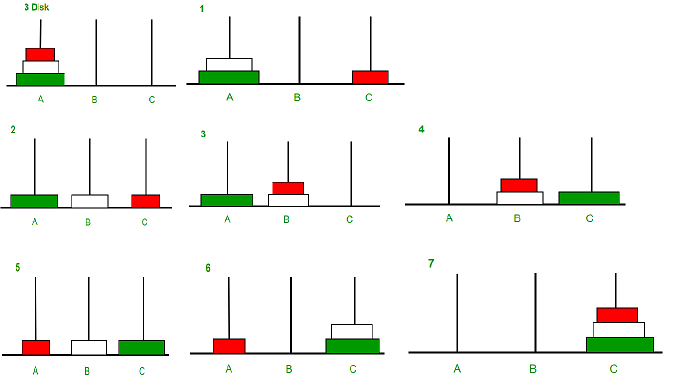
Tower of Hanoi
Tower of Hanoi is a mathematical puzzle where we have three rods and n disks. The objective of the puzzle is to move the entire stack to another rod, obeying the following simple rules:
- Only one disk can be moved at a time.
- Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the stacks and placing it on top of another stack i.e. a disk can only be moved if it is the uppermost disk on a stack.
- No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk.